The Scolty and Crathes oil fields are located in blocks 21/8a, 21/12c and 21/13a in the central North Sea sector of the UK Continental Shelf. The fields are jointly owned by EnQuest Heather (40%), MOL UK Facilities (50%) and Ithaca Energy (UK) (10%) and were developed by EnQuest, which is also the operator.
Located in water depths ranging between 95m and 105m, the fields are 9km apart and approximately 133km from St Fergus on the north-east coast of Scotland. The fields were developed at a cost of approximately $125m.
The field is anticipated to produce approximately 20,000bpd of fluids and have an expected life of 15 years.
Scolty and Crathes field development
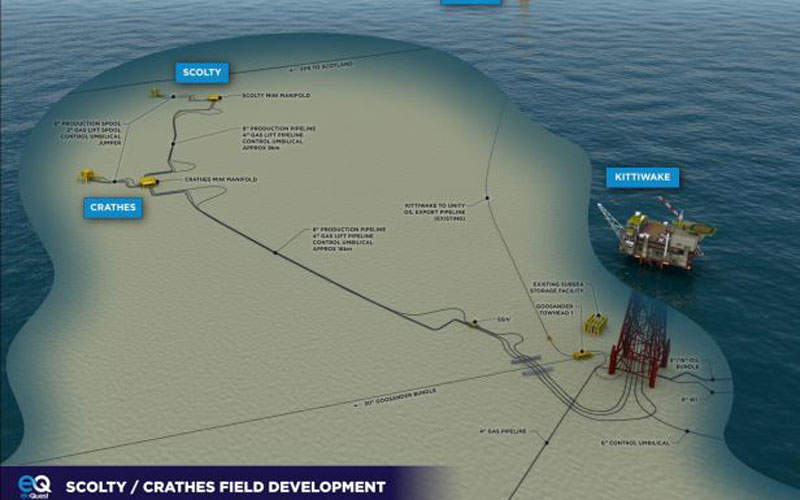
The field development plan (FDP) of Scolty and Crathes oil fields was approved in December 2015. It The Scolty/Crathes development is a subsea tie-back to the Kittiwake platform located in block 21/18 in the Greater Kittiwake Area, approximately 25km away.
The development includes drilling and completion of two producer wells and subsea facilities consisting of an 8in insulated production pipeline from the fields to the Kittiwake platform, a 4in gas lift supply pipeline from the Kittiwake platform to the wellheads, and an integrated electro/hydraulic control and chemical injection umbilical from the Kittiwake platform to the fields.
The two fields are linked with the Kittiwake platform in a daisy chain method by means of subsea production and gas lift pipelines. Fluids produced from the field are processed on the platform and then exported to shore through the Forties pipeline.
A hydraulic, electrical and chemical injection supply umbilical is used for controlling the fields from the host facility. A combination of water-based drilling mud and low-toxicity oil-based mud was used for drilling the wells.
Subsea infrastructure of Scolty and Crathes field
The subsea infrastructure comprises two mini manifolds, each consisting of a 6in production spool, 2in gas lift spool, jumper, and a control umbilical connecting to the production well Christmas tree formation.
Mini manifolds of the two fields are connected by an 8in production pipeline, a 4in gas pipeline and a control umbilical. An 8in production pipeline and a 4in gas lift pipeline and control umbilical are used to secure the Crathes mini manifold to the Kittiwake platform.
Discovery and reservoir details of Scolty and Crathes field
The Scolty field was discovered in 2007 by EnQuest upon drilling of well 21/8-3 in production license PL107. Crathes field was also discovered by EnQuest in 2011 by drilling of well 21/13a-5 in production licence PL617.
The Scolty field is a four-way dip closure at the top of the tertiary turbidite fan system and has a reservoir of good quality sandstone of Late Palaeocene/Early Eocene Cromarty Formation. The Crathes field is same as Scolty in size, depth and seismic character. Oil produced from the reservoir is a light variety with an API of 40°.
It is estimated to have gross peak volumes of 10,000 barrels of oil equivalent a day (boepd) in its first year, which is anticipated to increase EnQuest’s net 2P reserves by approximately nine million barrels.
Timeline
Drilling on the project began in the first quarter of 2016 and was completed in the second quarter of 2016. Installation and commissioning of the pipeline, subsea infrastructure and umbilicals was concluded in the fourth quarter of 2016.