Robotics is rapidly transforming oil and gas operations as advances in AI and cloud computing unlock the next phase of industrial automation. Robots can now operate autonomously, collaborate, and access cloud-based data in real time, enabling advanced decision-making, navigation in complex environments, and reduced reliance on human intervention. These capabilities are reshaping how oil and gas companies approach inspection, maintenance, and monitoring across upstream, midstream, and downstream operations.
Oil and gas operators are increasingly deploying robotics to improve safety, efficiency, and asset integrity. Subsea autonomous vehicles, robotic crawlers, quadruped robots, and hazardous-zone-certified inspection platforms are used to inspect pipelines, flare stacks, storage tanks, offshore platforms, and subsea infrastructure. Companies such as Equinor, Shell, BP, Chevron, TotalEnergies, Repsol, and ADNOC integrate robotics with AI, cloud computing, and advanced sensors to enable real-time analytics, predictive maintenance, emissions detection, and condition-based asset management.
According to GlobalData forecasts, the global robotics market was valued at $90.2bn in 2024 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 15% to reach $205.5bn by 2030. Service robots account for the largest share of the market, reflecting strong demand for inspection, monitoring, and maintenance applications in complex industrial environments. Oil and gas is emerging as a key contributor to this growth, as operators increasingly rely on robotics to address ageing infrastructure, workforce constraints, and heightened safety and ESG requirements.
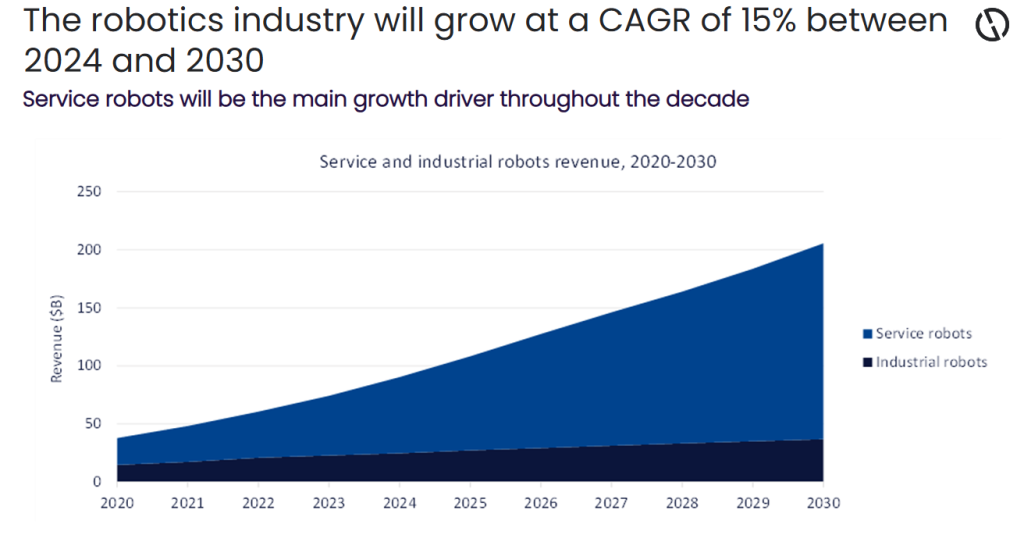
Robotics plays a critical role in offshore and subsea oil and gas operations, where harsh conditions, extreme pressures, and limited access make human intervention costly and risky. Beyond offshore environments, robotics enhances safety, efficiency, and sustainability across onshore operations. Robots are deployed in confined spaces, high-temperature areas, and zones with toxic or explosive gases, enabling rapid condition assessment and early intervention without endangering personnel. Despite its advantages, robotics adoption faces challenges related to capital investment, system integration, and operational reliability in extreme environments. However, the integration of robotics with digital twins, edge intelligence, and predictive analytics is driving a new era of smart operations. As these capabilities mature, robotics is expected to become a core pillar of automated, resilient, and sustainable oil and gas operations.
Further discussion on robotics adoption, key use cases, and competitive positioning can be found in GlobalData’s latest theme report, ‘Robotics in Oil and Gas’.
US Tariffs are shifting - will you react or anticipate?
Don’t let policy changes catch you off guard. Stay proactive with real-time data and expert analysis.
By GlobalData





