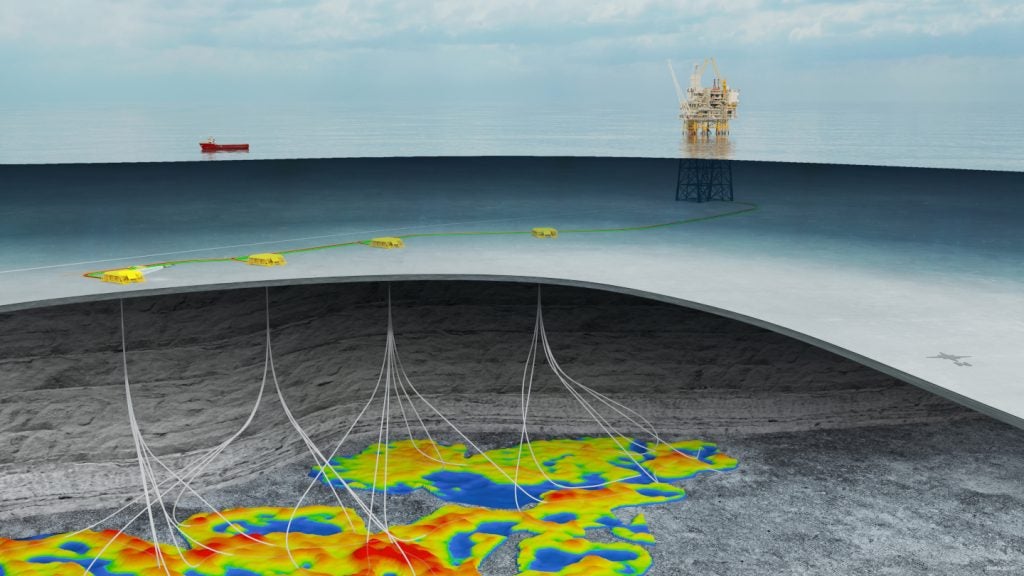
Katmai is a deepwater oil field development project, located at a water depth of approximately 1,820ft in Green Canyon blocks 39 and 40 in the US Gulf of Mexico.
The field is operated by Fieldwood Energy with a 50% working interest, with Ridgewood Energy holding the remaining interest in the field. It is expected to produce first oil in the second quarter of 2020.
Katmai oil field discovery and appraisal details
Katmai field was discovered in July 2014 by the then operator Noble Energy. A discovery well GC 40-1 was drilled to a total vertical depth of 27,900ft in 2,100ft of water in Green Canyon 40.
The well discovered a 154 net feet of crude oil pay in multiple reservoirs, including 117 net feet in Middle Miocene and 37 net feet of hydrocarbons in Lower Miocene sands. The total gross resources at the field were estimated to be between 40 and 100 million barrels of oil equivalent.
The appraisal well Katmai 2 was drilled in Green Canyon 39 at the Katmai oil discovery in 2016. It encountered high pressure in the unstudied portion of fault block, leading to its temporary abandonment.
Noble Energy initially held 50% working interest in the field, which was sold to Fieldwood Energy in 2018.
Development details of Katmai oil field
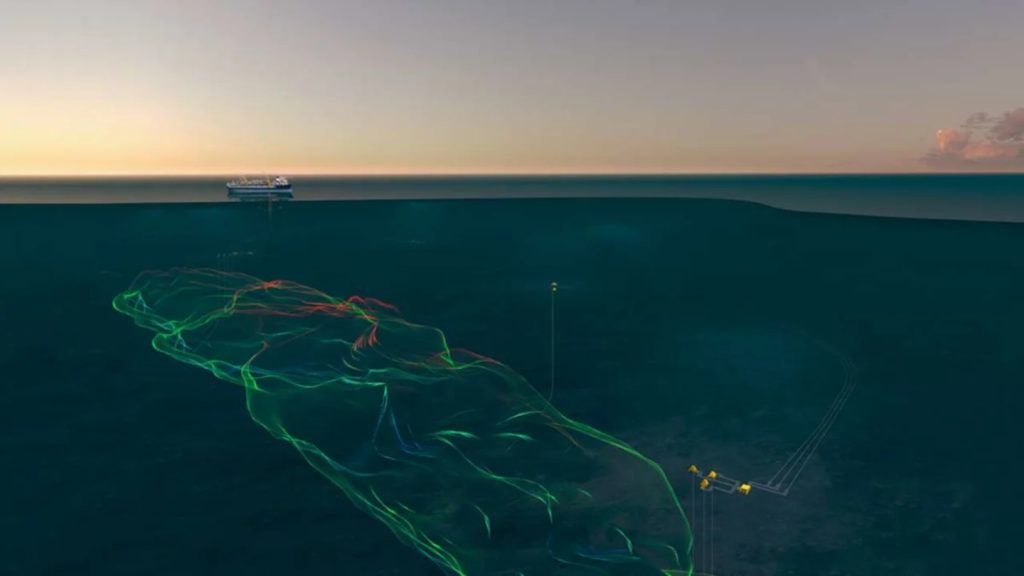
The Katmai oil field development involves the drilling of two wells, No.001 and No.002 (ST01), which will be tied back to Tarantula platform located in approximately 484ft of water depth in the South Timbalier Block 308 A in the Gulf of Mexico.
The wells will be controlled by the platform through 5.5in daisy-chained electrohydraulic umbilicals. The flowline of the Katmai field will begin at a pipe line-end-termination (PLET) point at the No.001 well and link to the No.002 (ST01) well via an in-line sled (ILS).
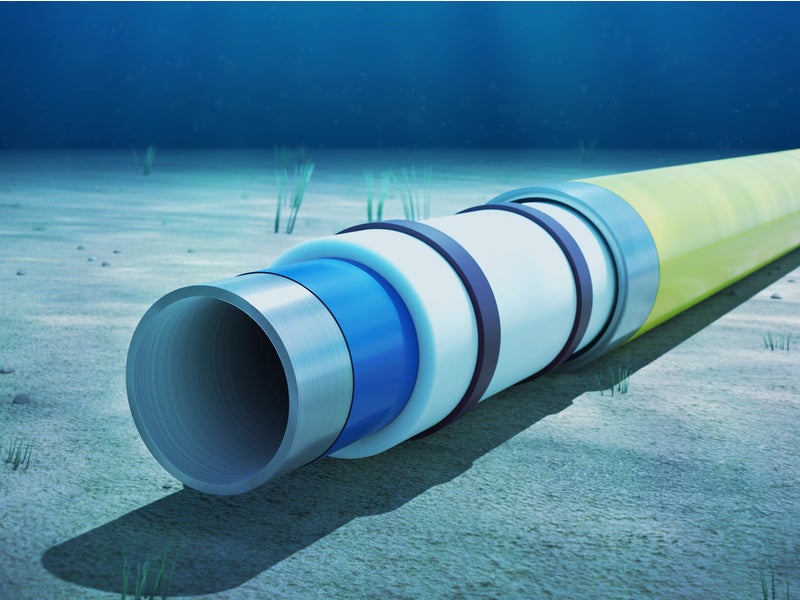
The design life of the subsea infrastructures is expected to be more than 20 years. A 40km-long pipe-in-pipe production flowline with 12in outer pipe and the eight-inch inner pipe was laid as part of the field development. Other subsea structures being installed are three trees, topside controls, valves, connectors, flying leads and umbilical termination assemblies.
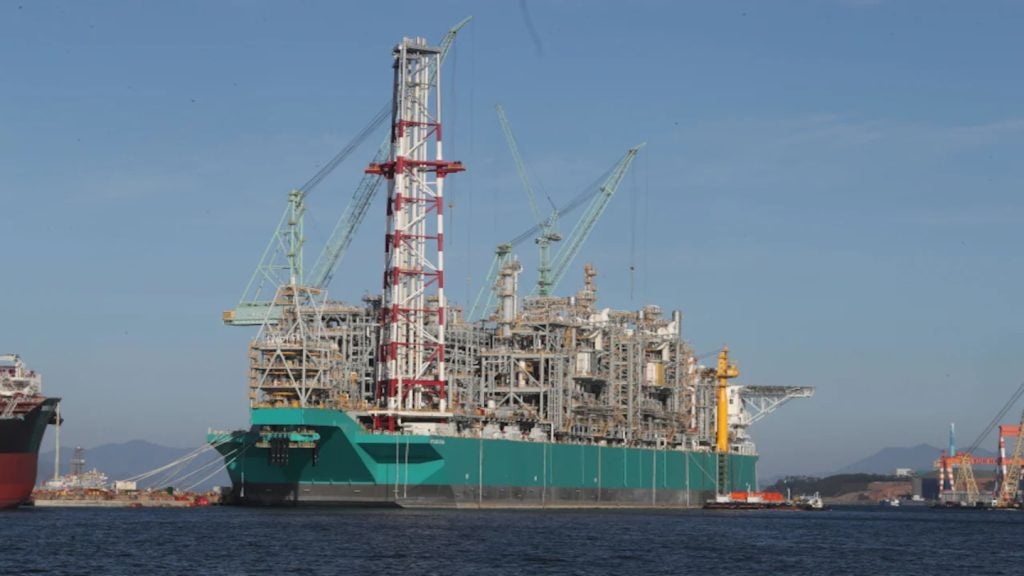
The oil produced from the field will reach the Tarantula production platform, which has the capacity to process up to 25,000 barrels of oil a day from the Katmai field development. The crude oil from the platform will be sent to the Poseidon crude oil system, 64% owned by Genesis Energy, via Tarantula lateral for onshore delivery.
Tarantula field details
Tarantula field was discovered by the drilling of a sub-salt discovery well to the total vertical depth of 18,000ft in 480ft deep water in July 2001. The field came onstream in 2005. The platform is a fixed four-legged structure with the processing capacity of 100 million cubic feet of natural gas per day and 30,000 barrels of oil per day.
A total of four wells were drilled in the field, encountering 117ft of net pay of hydrocarbons on an average.
Contractors involved in Katmai oil field project
Fieldwood Energy awarded the integrated engineering, procurement, construction and installation (EPCI) and project management contract to Subsea Integration Alliance, a partnership between Subsea 7 and Schlumberger’s OneSubsea, for the Katmai project, in October 2018.
Subsea Integration Alliance is leveraging the experience of Subsea 7 in subsea umbilicals, riser and flowline systems (SURF) and OneSubsea’s subsea production systems expertise for the field development. Genesis Energy won a contract to provide downstream transportation services for the crude oil produced from the field, in April 2020.