MJ field (also known as D55) is a gas condensate field located in a water depth between 700m and 1,100m in the KG D6 block of the Bay of Bengal, offshore India. The KG D6 block is jointly owned by Reliance Industries (60%, operator), BP (30%) and Niko Resources (10%).
The MJ project is part of the three KG D6 projects, including the R-Series and the Satellites cluster projects, which are being developed as part of the Block KG D6 integrated development plan with a total investment of $5bn.
The R-Series project is scheduled to commence production in mid-2020, while the Satellites cluster projects will begin in mid-2021 and the MJ field is expected to start production by mid-2022.
The three projects are collectively expected to produce an estimated three trillion cubic feet (tcf) of gas, which is equivalent to more than 10% of India’s projected gas demand in 2022.
MJ gas condensate field location
The MJ D55 gas condensate field is located in the Krishna Godavari basin of the Bay of Bengal offshore Andhra Pradesh, India. The Krishna Godavari basin covers an area of 15,000km² onshore and 25,000km² offshore.
The KG D6 block currently produces approximately 1.6 billion cubic feet of gas a day (bcf/d).
MJ gas field project discovery
The field was discovered in June 2014 by the KGD6-MJ1 discovery well drilled using the DD-KG-2 deep-water rig. The discovery well was drilled to a total depth of 4,509m in a water depth of 1,024m.
The well was drilled with the objective of exploring the Mesozoic Synrift Clastic reservoir, which lies 2,000m below the already producing reservoirs in the D1-D3 gas fields. The well encountered a gross gas and condensate column of 155m in the Mesozoic reservoirs.
During drill stem test, the well flowed at a rate of 30.6 million metric standard cubic feet per day (Mmscfd) and a liquid rate of 2,121 barrels a day.
The MJ gas field reservoir is a high-temperature and pressure reservoir.
MJ field appraisal details
The first appraisal well, MJ-A1, was drilled in 2014 and showed the presence of hydrocarbons. The second appraisal well, MJ-A2, was drilled in the same year to target the eastern fault block. It encountered a wet targeted section with high-quality Mesozoic synrift reservoir, similar to the one found in the MJ-1 discovery well and the MJ-A1 appraisal well.
The third appraisal well MJ-A3 was spud in 2015, which confirmed the presence of hydrocarbons in a third fault block of the structure, while the zone of interest was found to be thinner than expected.
MJ gas condensate field development details
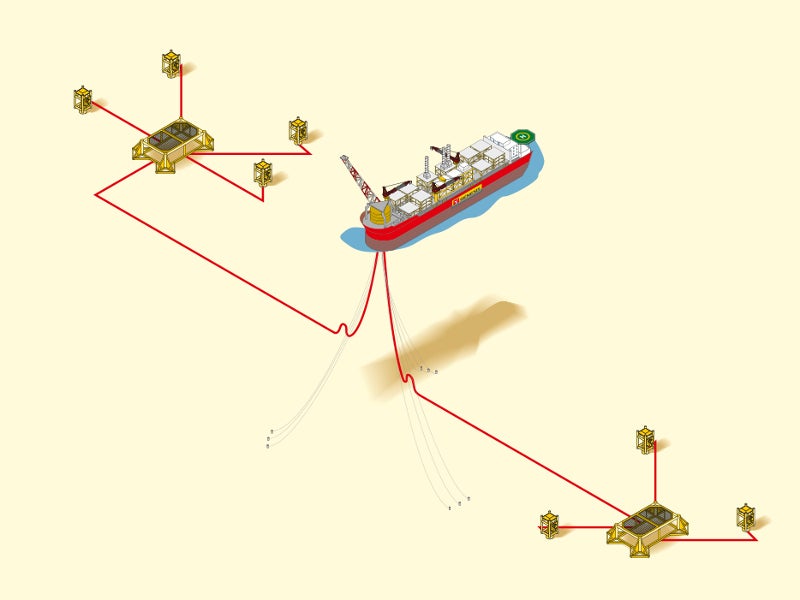
The project development plan includes the drilling of seven wells connected to two subsea drill centres that will be tied-back to a floating production, storage and offloading (FPSO) vessel.
The FPSO vessel will process and separate liquids and transport the gas to an onshore terminal through an existing 24in diameter pipeline.
MJ project will utilise the infrastructure being developed for the R-Series and Satellite projects.
DD-KG2 rig details
Dhirubhai Deepwater KG2 rig is an ultra-deepwater drillship manufactured by Samsung Heavy Industries in 2010.
The rig is classified as an ABS+A1(E) capable of operating at a water depth of 12,000ft to a maximum drilling depth of 35,000ft. It is equipped with an NOV dual dynamic Derrick with a two million pounds static load capacity.
The drillship can operate at a transit speed of up to 12 knots with accommodation for 180 persons.
Contractors involved
Genesis was awarded the deepwater front-end engineering design (FEED) contract for the MJ gas condensate field.