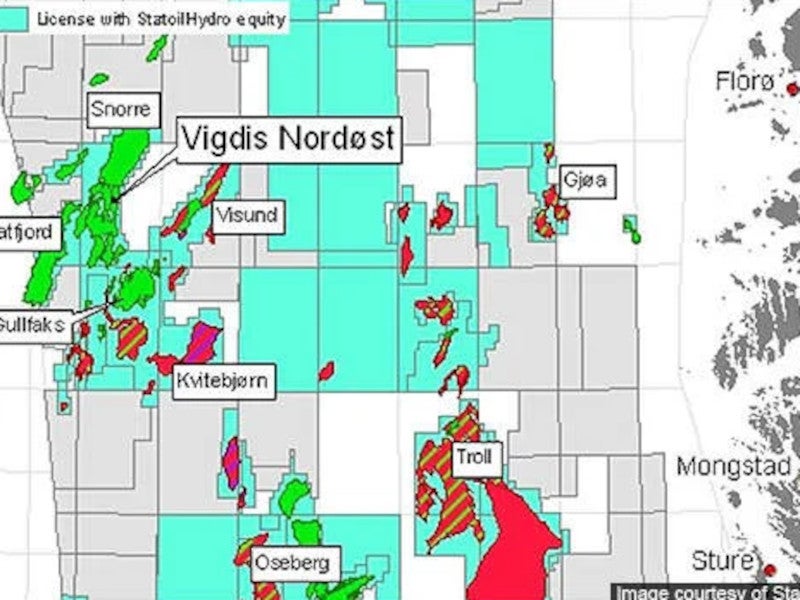
The Vigdis oil and gas field is situated in block 34/7 of the Tampen area in the North Sea, Norway at a water depth of 280m.
First production from Vigdis was achieved in 1997. Production from the Borg North-West (Vigdis extension) and Vigdis East discoveries commenced in 2003 and 2004 respectively.
In 2022, a plan for development and operation exemption was granted for the Lomre structure in the Vigdis field, which is expected to begin production in 2024.
Equinor is the operator of the field with an ownership of 41.5%. The other partners are Petoro (30%), Vår Energi (16.1%), Idemitsu Petroleum Norge (9.6%) and Wintershall Dea Norge (2.8%).
Vigdis discovery
Vigdis was discovered in 1986 by discovery well 34/7-8. In March 2009, additional reserves were discovered north of the Vigdis East field by an exploration well 34/7-34. The well was drilled by the Borgland Dolphin drilling rig and sidetracked to confirm the presence of hydrocarbons in the Statfjord group formation of the lower Jurassic age.
Oil reserves
Recoverable reserves at Vigdis were estimated at 475 million barrels (mbbl) of oil as of 2021.
Reservoir details
Oil from Vigdis is produced from sandstone in several structures. The Vigdis Brent and Lomre reservoirs are in the Middle Jurassic Brent Group. The Vigdis Øst-Nordøst is in the Upper Triassic and Lower Jurassic Statfjord Group while the Borg Nordvest reservoir lies in Upper Jurassic intra-Draupne sandstone.
The reservoirs have generally good quality and are located at depths of between 2200 and 2600 metres.
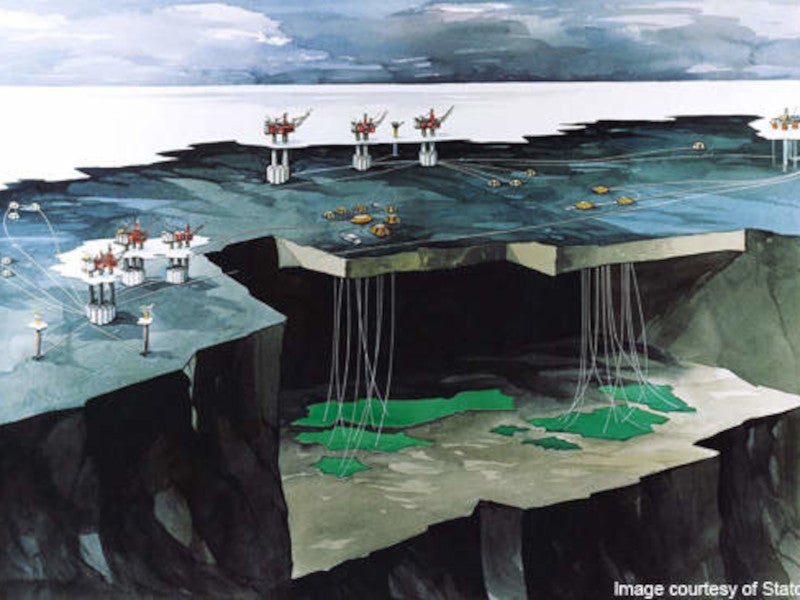
Vigdis field development
The Vigdis gas and oil field is comprised of four structures: Vigdis Brent, Borg Nordvest, Vigdis Øst-Nordøst and Lomre. The Vigdis Brent structure comprises several substructures.
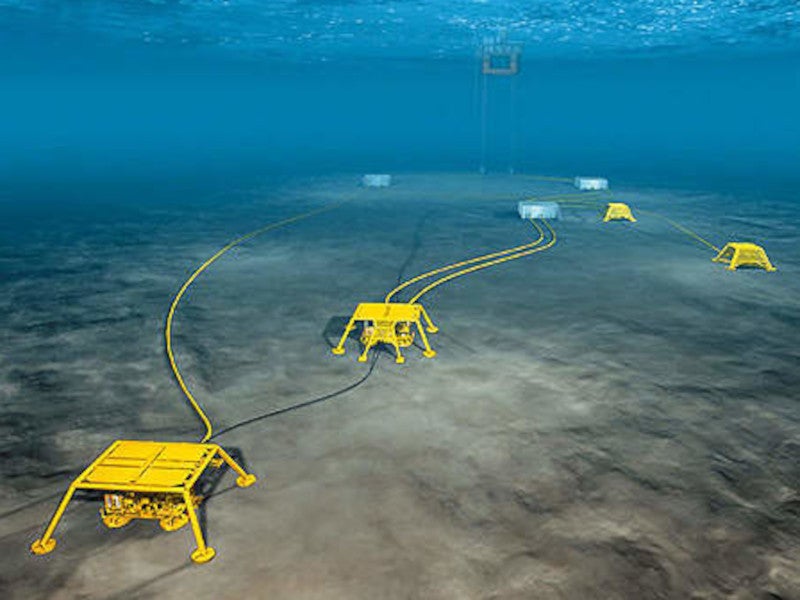
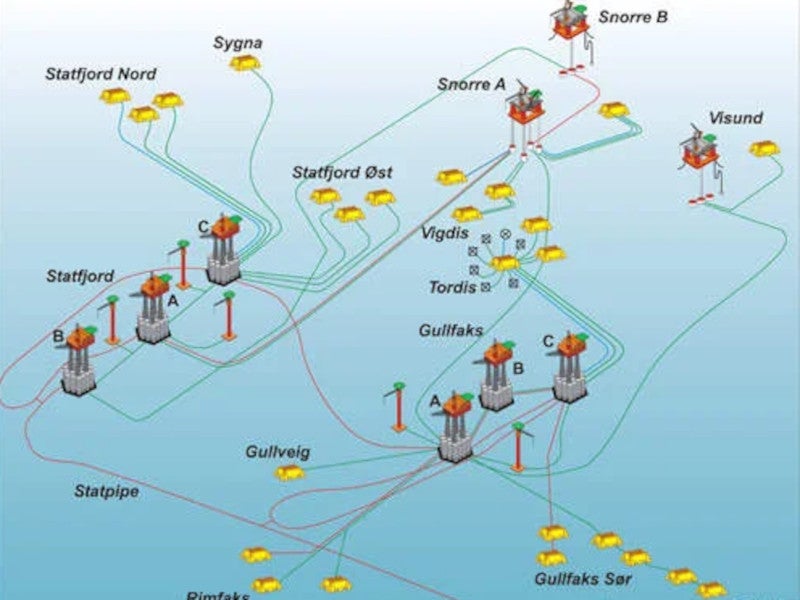
The Vigdis field has been developed with seven subsea templates and two satellite wells connected to the Snorre A facility.
In 2020, a subsea booster pump was installed to increase production efficiency at the Vigdis field. The pump on the seabed provides the Vigdis oil field in the North Sea with a boost that increases production by around 16mbbl.
A total of 12 wells, including four injection wells, were drilled to develop the fields. The subsea equipment is tied back to the Snorre A tension leg platform at the Snorre oil field, which is located 7km away.
The Borg North-West and the Vigdis East fields were developed in two phases under the Vigdis extension project. The extension enabled the recovery of an additional 50mbbl of oil.
Phase one of the extensions included the installation of two seabed templates and two satellite structures on the Borg North-West field. Three production and three injection wells were drilled during this phase.
Phase two required an investment of $180m. A third template was installed, and one production and one water injection well were drilled on the Vigdis East field during this phase. The template featuring four well slots commenced production in April 2008.
Snorre A tension leg platform
Snorre A has been operating in the Snorre field since 1992. It is installed at a depth of 305m and moored by a steel tethered system. It features a separate processing module to process the well stream produced at the Vigdis field.
Production and export
Oil is recovered by applying partial pressure on the reservoir through water injection. It is processed at the Snorre A platform and transported to the Gullfaks A platform for storage and export through pipelines. Gas recovered at the main Vigdis field is injected into the Snorre field reservoir.
Gas recovered from the Borg North-West and Vigdis East fields is sent to Snorre A and Statfjord A platforms for processing.
The processed gas is transported by the Statpipe / Norpipe system to different markets.
Contractors involved
Engineering and consulting company Wood secured a $13m contract in February 2019 with Equinor to provide engineering, procurement, construction and installation services for the Vigdis boosting station’s increased oil recovery project.
Equinor awarded DeepOcean, a subsea services provider, the contract for marine operations to install the Vigdis boosting station in May 2019.
NKT Flexibles, a Denmark-based flexible cable supplier, provided two water injection replacement lines, jumpers and flowlines for the Vigdis field and the Vigdis extension project.
Pumping systems manufacturer, Framo Flatøy was contracted to supply the boosting system supply for the Vigdis field expansion project. The supply scope included a subsea template and trawling protection. RadøyGruppen, a complete fabrication, construction and integration service supplier, fabricated the subsea template while Luster Mekaniske Industri supplied the pipelines. Theta Norge provided consultancy services for the laying of the Vigdis subsea flow lines.
In December 2010, FMC Technologies won a $75m contract for supplying subsea equipment for the Vigdis North-East field. The contract included the supply of subsea trees, a manifold, an umbilical and other equipment.
FMC Technologies supplied subsea equipment for phase two of the Vigdis extension project under a $25m contract awarded in 2006. The equipment included four subsea trees, a manifold and control system, a subsea control cable and a control system. The company also provided system integration, installation and maintenance services.
Statoil undertook an upgrade programme called the Tordis Vigdis controls modification (TVCM) project for the Tordis and Vigdis fields. In June 2009, GE Oil & Gas was awarded a $70m contract to supply its VetcoGray SemStar5 subsea control module for the fields.
ClampOn, a non-intrusive sensor manufacturer for topside and subsea applications, was contracted to supply funnels and sensors for the subsea modules of the TVCM project.
In 2002, Stolt Offshore was awarded a Nkr535m contract to supply 23km of 6in and 12in flowlines and umbilicals.