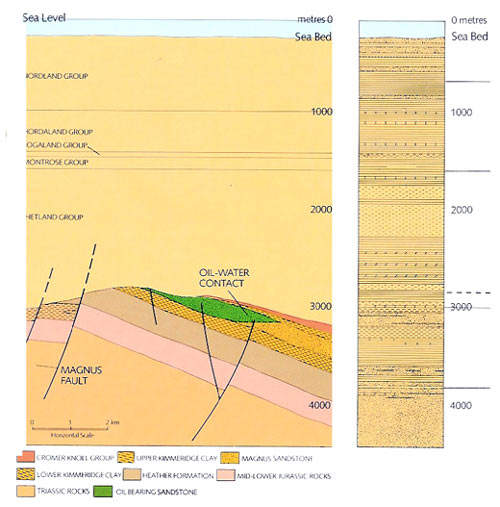
Magnus – the UK’s most northerly oilfield – was discovered in 1974 by the semi-submersible drilling rig Sedco 703. It lies 160km north-east of the Shetlands in block 211/12a. Oil was found 2,709m below the seabed in a water depth of 186m. Reserves are estimated at 1.65 billion barrels of oil, 797 million of which are expected to be recovered (48%). Magnus came on stream in 1984 and is currently producing around 67,000bpd.
The Magnus enhanced oil recovery project was developed as a single central combined drilling and production platform of conventional steel. Produced oil is transported through a 24in crude oil pipeline to the Ninian Central platform while gas is piped ashore using a joint pipeline linked to the Shell/Esso Far North Liquid and Associated Gas System (FLAGS), which runs to St. Fergus.
EXTENDED PRODUCTION
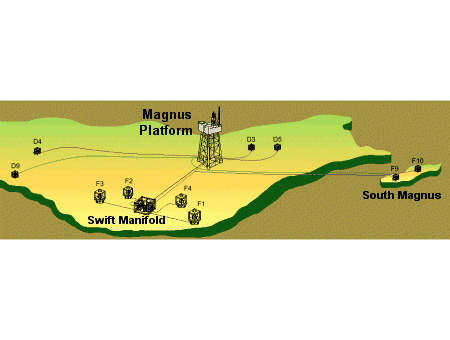
A number of options have been considered for extending the production life of Magnus. First component of the overall Magnus Exploitation Project was the Swift (subsea water injection facilities and tieback) project. Swift involved tying subsea water injection wells back to the Magnus platform by means of a ‘mini’ manifold for up to seven water injection wells, a subsea flowline and umbilical.
Phase 1 became operational in May 1996. It consists of one development well tied back 7km to the Magnus platform with a water injection well tied in to the Swift flowline. Recoverable reserves are estimated to be 20 million barrels of oil and 26 billion cubic feet of gas. Anticipated field life is ten years.
SOUTH MAGNUS
South Magnus production to the main platform is through a 5.6in internal diameter, 7km flexible flowline. A water injection well provides reservoir pressure support and injection water is provided from Magnus via the Swift flowline through a 7in internal diameter flexible flowline. There is provision for the addition of further production wells in the future if required.
MAGNUS EOR
The latest stage of the Magnus field regeneration is the enhanced oil recovery (EOR) project that will involve importing gas from the deepwater Foinaven and Schiehallion fields and reinjecting it into the Magnus reservoir. The aim is to increase Magnus reserves by some 50m barrels of oil and extend the field life by several years to beyond 2015.
The Magnus Enhanced Oil Recovery Project will bring surplus gas through a new 400km pipeline, 110 miles west of Shetland. The Foinaven field lies in a water depth of between 400 and 600m. The Schiehallion and adjacent loyal field lie predominantly in 204/20 and 204/25, 175km west of Shetland in a water depth of between 350 to 450m.
The 400+km pipeline project will pipe gas from the two fields to a landfall at Sullom Voe in the Shetlands where NGLs will be added. The gas will then be pipelined to the Magnus oilfield in the North Sea, where it will be re-injected to act as a miscible injectant to improve oil recovery rates. The project will cost BP and its partners around £320 million. Gas from Foinaven and Schiehallion is currently reinjected. In addition to the installation of an additional compressor on Magnus, the work will involve modifications on Foinaven and Schiehallion and to an existing plant at Sullom Voe.
Fugro carried out a major integrated pipeline route survey for BP for the Magnus EOR Project. This was followed by an initial geophysical and bathymetric reconnaissance survey over a wide survey corridor to best define a suitable route for the pipeline, using Fugro’s vessel Geo Scanner.
Although the project contains no new offshore platform, approximately £300 million is being invested in the 250 mile long main and branch pipelines, subsea tie-ins and modifications on the Magnus platform and at the terminal. In addition to the ongoing engineering support work by Wood Group and Amec, contract awards have been made to:
- Bredero Price Coaters – pipe coating
- Stolt Offshore – subsea construction and diving support
- Wood Group – platform modifications
- Amec – modifications at SV terminal
- Halliburton – subsea construction and ROV support
- J P Kenny – pipeline design and procurement services
- Kvaerner Oil & Gas – subsea control system design and supply
- McGregor Energy Services – fabrication of subsea hardware
- BEL Valves – valve supply