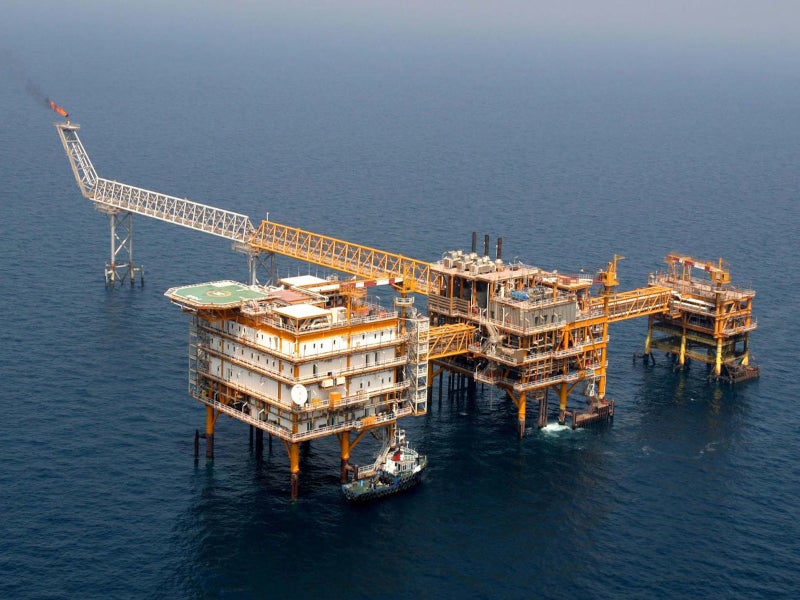
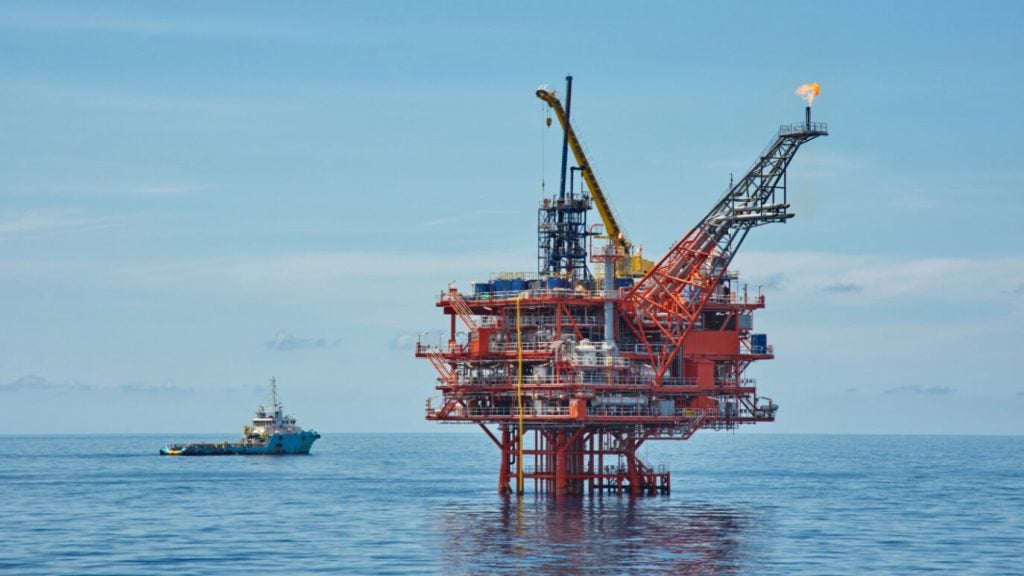
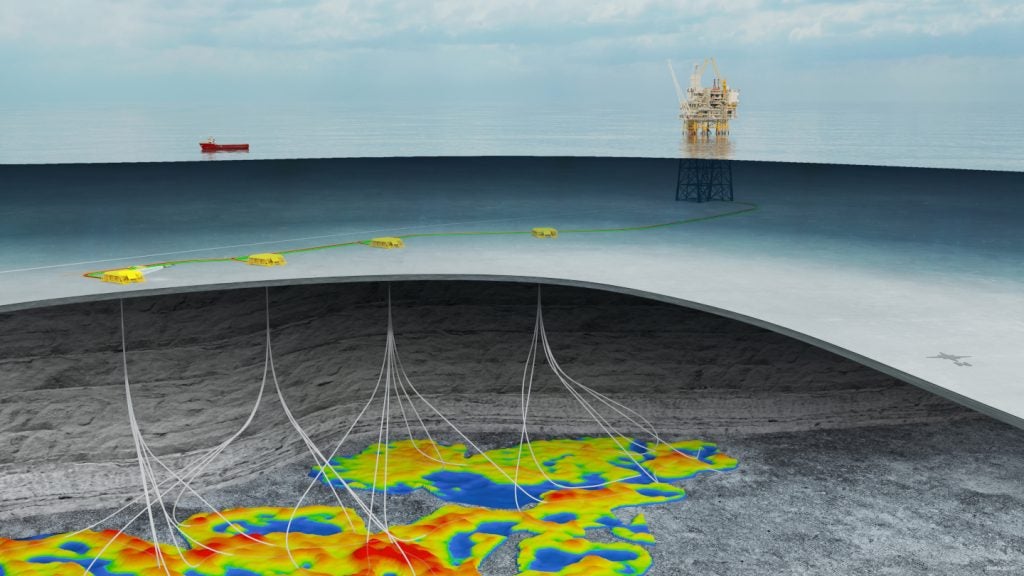
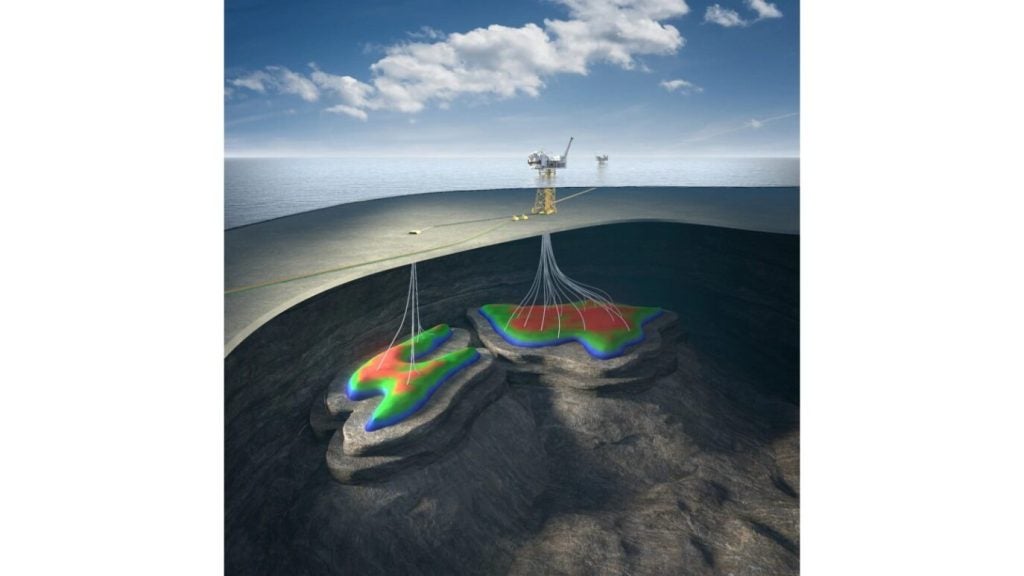
Farzad B is a gas and condensate field located at water depths ranging from 20m to 90m within the Farsi block in the Persian Gulf, offshore Iran.
Spanning 3,500km², the Farsi offshore exploration block is owned by the National Iranian Oil Company (NIOC), a state-owned natural gas company.
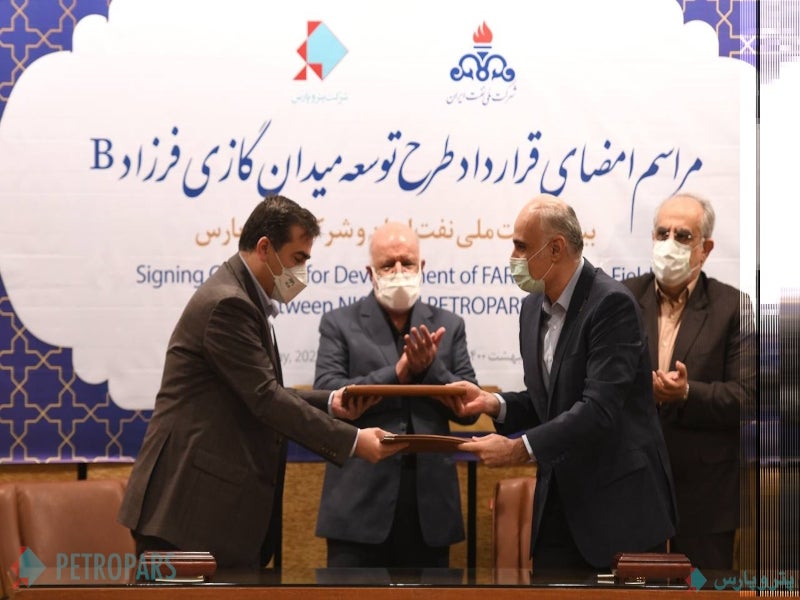
NIOC awarded a $1.78bn contract to local oil and gas company Petropars Group for the development of the Farzad B field in May 2021. The buyback contract will target a daily production rate of 28 million cubic metres (Mm³) of sour gas over five years. The field is expected to produce one billion cubic feet of gas a day (Bcfd) within five years.
Farzad B gas project development history
An Indian consortium led by Oil and Natural Gas Corporation Videsh (OVL, 40%) and overseas arm of India’s national oil company ONGC, was awarded an exploration service contract (ESC) to explore the Farsi block, in December 2002.
The consortium also included Oil India (20%) and Indian Oil Corporation (IOC, 40%). It discovered the Farzad B gas field in August 2008. The exploration phase of its contract with the NIOC expired in June 2009.
A $3bn master development plan for the field was submitted by OVL to the Iranian authorities in April 2011. The Indian and Iranian authorities continued the negotiations over the development service contract (DSC) until November 2012.
The DSC was, however, not concluded due to the imposition of international sanctions on Iran. The parties resumed discussions in 2015, but the reimposition of US sanctions on Iran from November 2018 put an end to technical studies on the field.
Location, geology and reserves
The Farzad B gas field is located 35km away from Farzad A field and 85km east of Bushehr. It straddles the Iran-Saudi Arabia maritime border.
The field has a high pressure of 9,000psi and a high temperature of 130°. The fractured and faulted geology and reservoir gas composition add to the development challenges of the field, which has a complicated geological structure.
A high-quality 2D seismography was conducted in the field, which helped in achieving valuable information on the tank upper status.
The Iranian waters of the Farzad B field are estimated to hold natural gas reserves of about 23 trillion cubic feet (Tcf), of which 212 million barrels of condensate and 12.8Tcf of gas are recoverable.
Farzad B field development details
The development of the Farzan B gas field will involve the drilling of eight production wells and the construction of a main and a secondary wellhead platform. Liquid separation facilities will be installed on the main platform. A 3km-long, 20in-diameter pipeline will be laid to interconnect the three platforms.
Furthermore, a 230km-long, 36in-diameter sub-sea pipeline will be installed to transfer sour fluid from the main platform to onshore facilities while another 230km-long, 10in-diameter pipeline will be used to transport condensate to land-based infrastructure.
The offshore facilities will comprise the equipment to separate the produced sour fluid and condensate, along with ancillary facilities. The project will also involve the construction of onshore pipelines to transfer and distribute sour gas and condensate to refineries located in the Pars 2 region in Kangan for further processing.
The gas condensate will be separated from the sour gas in the onshore facility and further transported to the refineries built under phases 12 and 19 of the South Pars natural-gas condensate field in the Persian Gulf, for stabilisation.