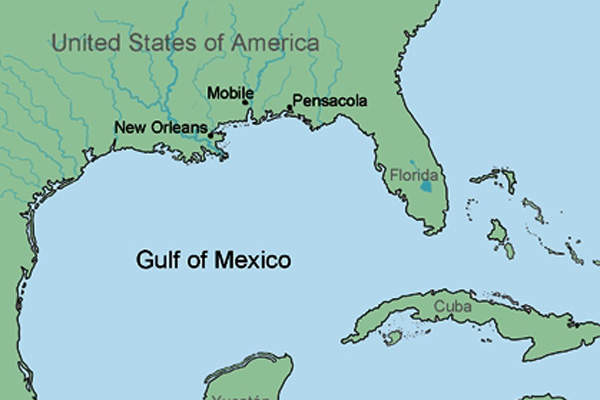
Stones field is situated in Block 508 in the Walker Ridge area of the Gulf of Mexico, around 322km off the coast of New Orleans, Louisiana, US. The ultra-deepwater project lies in a depth of approximately 2,900m. The field is owned and operated by Royal Dutch Shell.
The Stones field is estimated to hold more than two billion barrels of oil equivalent (boe). Production from the field was achieved in September 2016. The field hosts the deepest FPSO installation in the world.
Discovery and drilling of Stones field
Situated near the St Malo, Cascade and Chinook developments in the Gulf of Mexico, Stones field was discovered in 2005. The Stones-2 well was drilled in 2005 to a depth of 8,705m. The Stones-3 exploration well drilled in 2008 reasserted the multiple oil-bearing sands.
Stones ultra-deepwater field development
Shell made the decision to invest in the Stones field development project in May 2013. The first phase of development includes two subsea wells tied back to a floating production storage and offloading (FPSO) vessel. Six more development wells will subsequently come on stream, raising the production capacity of the field. The first phase of development is expected to reach a peak production capacity of 50,000boe/day by the end of 2017 from more than 250,000boe of recoverable reserves.
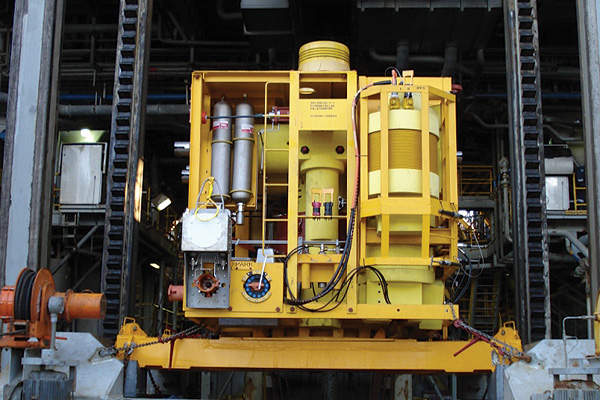
FMC Technologies was awarded the contract by Shell in May 2013 to supply subsea equipment to support the development of Stones field. The contract includes the delivery of eight subsea trees, a subsea manifold, topside and subsea controls, and other related equipment.
Front-end development work for the Stones FPSO vessel was started by Shell and SBM Offshore in 2011. Shell placed a supply and lease contract with SBM Offshore for an FPSO vessel for the Stones development project in July. The Stones FPSO is the first vessel to be deployed under an enterprise framework agreement signed in March 2012, for the delivery of medium and small FPSOs on a lease and operate basis.
Technip received an additional subsea contract from Shell in October 2015 to develop subsea infrastructure for the Stones field. The scope of the contract includes engineering of the second pipeline end terminations (PLETs), fabrication of the PLETs and piles, and installation of the subsea production system.
Stones FPSO details
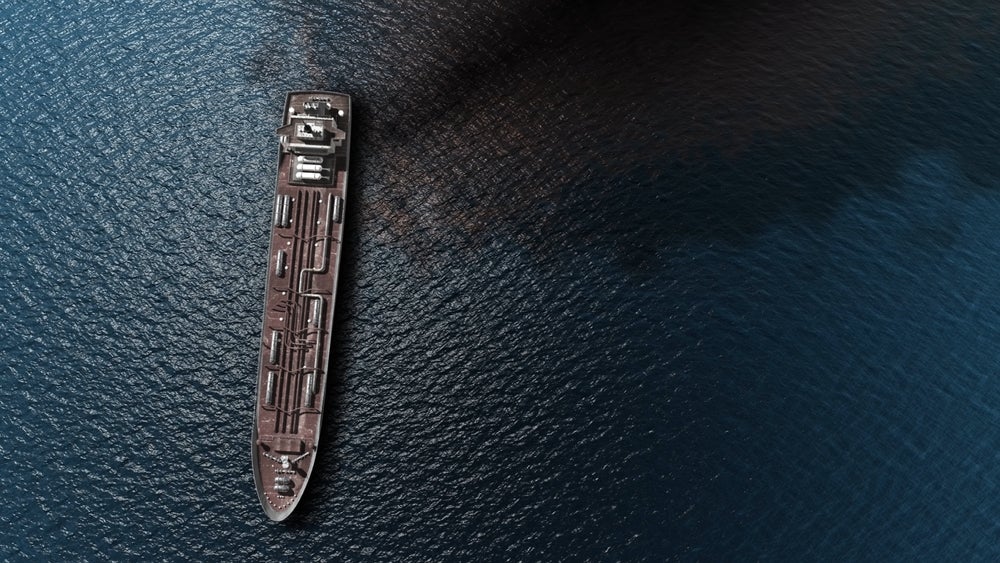
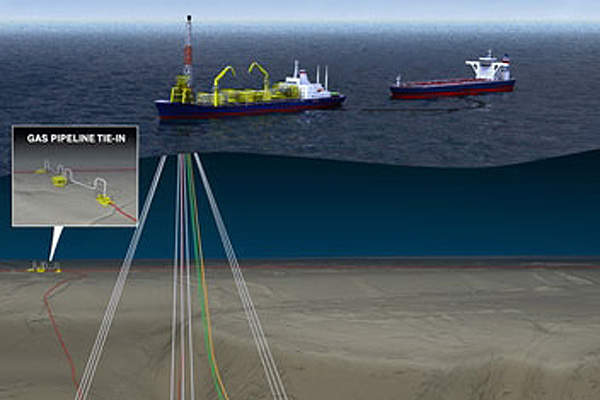
The FPSO used for the Stones field is a converted Suezmax tanker. It is secured using buoyant turret mooring (BTM) technology. The disconnectable buoy-equipped turret enables the vessel to vane on location or disconnect from the well in the event of adverse weather. The steel lazy wave risers linking the subsea systems to the BTM are being used for the first time with a disconnectable FPSO.
The FPSO vessel has the capacity to process oil at a rate of 60,000 barrels a day and gas at a rate of 15 million standard cubic feet a day. The Suezmax hull can store approximately 800,000 barrels of crude oil.
The FPSO design concept was chosen to safely produce oil from the Stones ultra-deepwater prospect. The FPSO solution also addresses issues related to the lack of infrastructure, complexness of the seabed, and unique reservoir characteristics. The oil from the FPSO is transported to US refineries using tankers, while gas is shipped through a pipeline.
Shell’s Lower Tertiary exploration and developments
Lower Tertiary refers to the ultra-deepwater region in the Gulf of Mexico. Shell became one of the innovators in the Lower Tertiary, after establishing first production from its Perdido Development in 2010.
The development of the Stones field extends the deepwater exploration and development efforts of Shell in the Gulf of Mexico. The company recently accomplished significant progress on the Mars-B development after the deployment of the Olympus tension leg platform. Appomattox and Vito prospects in the same region are both in the concept selection phase as of July.
Related content
Atlantis Deepwater Oil and Gas Platform, Gulf of Mexico, United States of America
Considered one of BP’s most technically challenging projects ever, the Atlantis platform is the deepest moored floating dual oil and gas production facility in the world.
Who Dat Field, Gulf of Mexico, United States of America
The Who Dat oil and gas field is located in the Mississippi Canyon (MC) blocks 503/504/547 of the Gulf of Mexico (GOM).